Your personal information, once considered safe, is now a prime target for cybercriminals. They are constantly seeking vulnerabilities to exploit, leaving you exposed to identity theft and financial loss.
Wondering what’s the best way to stay secure from data breaches? Just try your best to prevent them, through some careful practices. The guide explores what a data breach is, its potential impact, and how you can prevent it.
What is Meant by Data Breach?
A data breach occurs when sensitive or confidential information is stolen or taken from a system without the knowledge or permission of the owner. This can happen to anyone or any organization, from small businesses to large corporations and government agencies.
Types of data that can be breached include:
- Personal information, including names, addresses, Social Security numbers, credit card numbers, and other identifying information.
- Financial information including, bank account numbers, credit card numbers, and other financial data.
- Medical information usually includes health records, insurance information, and other medical data.
- Intellectual property such as trade secrets, patents, and other proprietary information.
- Customer records, which have customer lists, purchase histories, and other customer data.
10 Most Common Data Breaches You Could Be the Target Of
Staying online has made our lives convenient, but it has also made us more vulnerable to data breaches. These breaches can happen to anyone, from individuals to large corporations. Here are some common scenarios where you could be a target:
1. Weak or Reused Passwords
This is the most common cause of data breaches. Cybercriminals use automated tools to crack weak passwords or try common combinations. If you use the same password for multiple accounts, a breach in one can compromise them all. You can use a solid password manager to mitigate this issue.
2. Phishing Attacks
Phishing emails or messages are designed to trick you into revealing sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or social security numbers. They often appear to be from legitimate sources, such as banks or government agencies.
3. Malware Infections
Malware, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware, can infect your devices and steal your personal information. It can happen through malicious downloads, infected emails, or visiting compromised websites.
4. Data Breaches at Companies You Use
Many companies store your personal information, such as your name, address, and financial details. If these companies experience a data breach, your information could be exposed.
5. Social Media and Online Activities
Cybercriminals often exploit social media platforms and online forums to gather information. They can use your posts, comments, and photos to learn about your habits, interests, and personal details.
6. Poor Security Hygiene
Not using strong passwords, failing to update software, and neglecting security measures like firewalls and antivirus software can make you an easy target for cybercriminals.
7. Insider Threats
In some cases, data breaches can be caused by employees or contractors with access to sensitive information. They may intentionally or unintentionally leak information.
8. IoT Devices
Internet-connected devices like smart TVs, smart speakers, and security cameras can be vulnerable to attacks. If these devices are not properly secured, they can be used to access your network and steal your data.
9. Public WiFi
Using public WiFi networks without a VPN can expose your internet traffic to hackers. They can intercept your data and steal sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers.
10. Mobile Devices
Mobile devices like smartphones and tablets are often used for online banking, shopping, and social media. If your device is lost or stolen, your data could be compromised.
How to Know If Your Personal Information is Part of a Data Breach
To determine if your personal information has been compromised in a data breach, you can use the following methods:
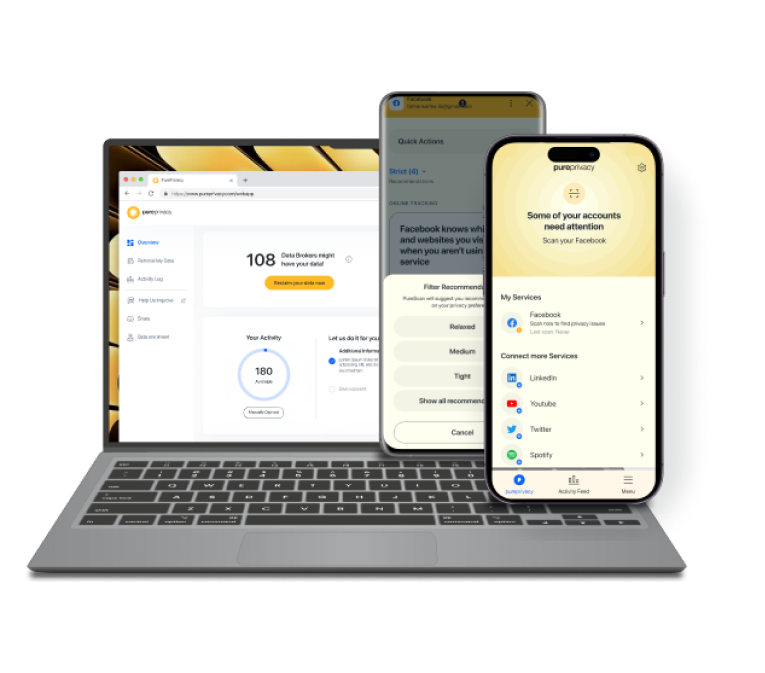
1. Use Privacy Management Services
Using a privacy management service can help you detect if your data is compromised. PurePrivacy gives you a personalized privacy score and highlights where your information has been shared online.
Plus, many credit monitoring services, like those offered by credit bureaus, can alert you to potential identity theft or data breaches that may impact your financial information.
2. Monitor Your Accounts for Unusual Activity
Regularly check your email and bank accounts for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized transactions or unfamiliar login attempts. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
3. Be Wary of Phishing Attempts
Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources and be cautious of unsolicited emails or phone calls requesting personal information. Also, it is important to verify the sender's identity before responding to any communication.
How Do Data Breaches Happen?
Data breaches occur due to a variety of factors, including weak security practices, human error, cyberattacks, and insider threats. Weak passwords, outdated software, and a lack of robust security measures can make systems vulnerable to attack.
Human error, like accidentally sharing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links, is another common cause of breaches. Cyberattacks, including phishing, malware, and ransomware, exploit system vulnerabilities to steal data.
Insider threats, where employees or contractors misuse or sell sensitive information, pose another risk. These breaches can have severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties.
What are the Consequences of Data Breaches?
The consequences of data breaches can be severe for both individuals and organizations. One of the most alarming aspects of data breaches is the potential for stolen data to end up on the dark web. Here are some common concerns if your data has been breached:
- Identity Theft
Stolen personal information, such as Social Security number (SSN), credit card details, and addresses, can be exploited to open new accounts, make fraudulent purchases, or take out loans in the victim's name. For organizations, a data breach can result in substantial financial costs, including legal fees, regulatory fines, loss of revenue, and the cost of incident response and recovery efforts.
- Financial Loss
You may experience financial losses due to unauthorized transactions, fraudulent charges, and the need to repair damaged credit.
- Reputational Damage
A data breach can severely damage an organization's reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and business and they may face legal action from affected individuals, regulators, and shareholders.
- Operational Disruption
Data breaches can disrupt business operations, leading to system downtime, productivity loss, and potential service disruptions.
7 Effective Tips to Prevent a Data Breach
Data breaches are becoming increasingly common, and their consequences can be severe. To protect your personal information, it's essential to just follow some common tips and stay secure.
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Create complex passwords that include a variety of characters, such as uppercase, lowercase, and numbers. Use a different password for each account. You can also consider using a password manager to securely store and generate strong passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such 1 as a code sent to your phone or a security token.
- Keep Your Software Updated
Regularly update your operating system, web browsers, and other software to patch vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit.
- Be Cautious of Phishing Attacks
Be wary of suspicious emails, texts, or phone calls that ask for personal information or urge you to click on links. Never share sensitive information with unknown senders.
- Use Secure WiFi Networks
It is better to avoid public WiFi networks for sensitive activities like online banking or shopping.
Use PureVPN to encrypt your internet traffic so that you stay secure.
- Dark Web and Social Media Monitoring
Your data is not even secure on social platforms. You are at risk of data theft that could be used on the dark web. PurePrivacy helps you manage your information shared online. With its social monitoring and dark web scan, you stay informed about where your information has been shared.
- Use Secure Browser
Using a privacy-focused browser is important! You must try to use those browsers that offer strong privacy settings.
What to Instantly Do If Your Information is Stolen?
If you suspect your personal information has been compromised, it's crucial to take immediate action to minimize potential damage.
- Identify the Breach
Determine how your information may have been exposed (e.g., data breach, phishing email, lost device). Consider the types of information stolen (e.g., Social Security number, credit card details, bank account information).
2. Secure Your Accounts
Update passwords for all online accounts, especially those linked to the compromised information. Add an extra layer of security to your accounts through 2FA and keep a close eye on your bank and credit card statements for unusual activity.
3. Contact Financial Institutions
Inform your bank, credit card companies, and other financial institutions about the incident and request a fraud alert on your credit report to prevent new accounts from being opened in your name. Plus, enable a credit freeze to prevent new credit from being issued in your name.
4. Report Identity Theft
Contact your local law enforcement agency to file a report. You must also file a complaint with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) at IdentityTheft.gov. t you to phony websites.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Is data breach a cybercrime?

Yes, data breaches are cybercrimes. Cybercriminals may hack into systems, steal sensitive information, and sell it on the dark web. This can lead to criminal charges and severe penalties.
-
Is my data safe on Facebook?

No. Your data isn’t secure on social media. Facebook has a history of data privacy issues and breaches. While they have implemented measures to improve security, it's important to be cautious and take steps to protect your data, such as reviewing your privacy settings, limiting information sharing, using strong, unique passwords, and enabling two-factor authentication.
-
Can my data be stolen from Google?

Yes. Like any other online service, Google can be a target for cyberattacks. While Google has robust security measures in place, it's still possible for data breaches to occur.
-
What is the biggest data breach in history?

The largest data breach in history is often attributed to the 2013 Yahoo data breach, which affected over 3 billion user accounts. This massive breach exposed a vast amount of personal information, including names, email addresses, and passwords.
In Summary
A successful breach can lead to the loss of valuable intellectual property, sensitive customer data, and other critical information. The financial and reputational consequences of such incidents can be severe. The right tools are essential for effective data breach prevention. Plus, encryption and privacy management could be a great help!