Table of Content
No individual or company is secure from online data breaches!
And there are tons of data breaches happening every single day and some of the news don’t get to be in the spotlight.
The magnitude of online data breaches and scams are serious and scary.
Last month in August, a popular hacking group hacked an online company that offers background checks, and it exposed almost 3 billion individual records.
In 2024, over 35.9 billion records have been breached in 9,478 publicly disclosed incidents globally.
The frequency and amount of illegal access to personal information have risen due to weak passwords and human errors.
The present situation highlights the importance of proactive private data protection.
What can you do to protect personal data?
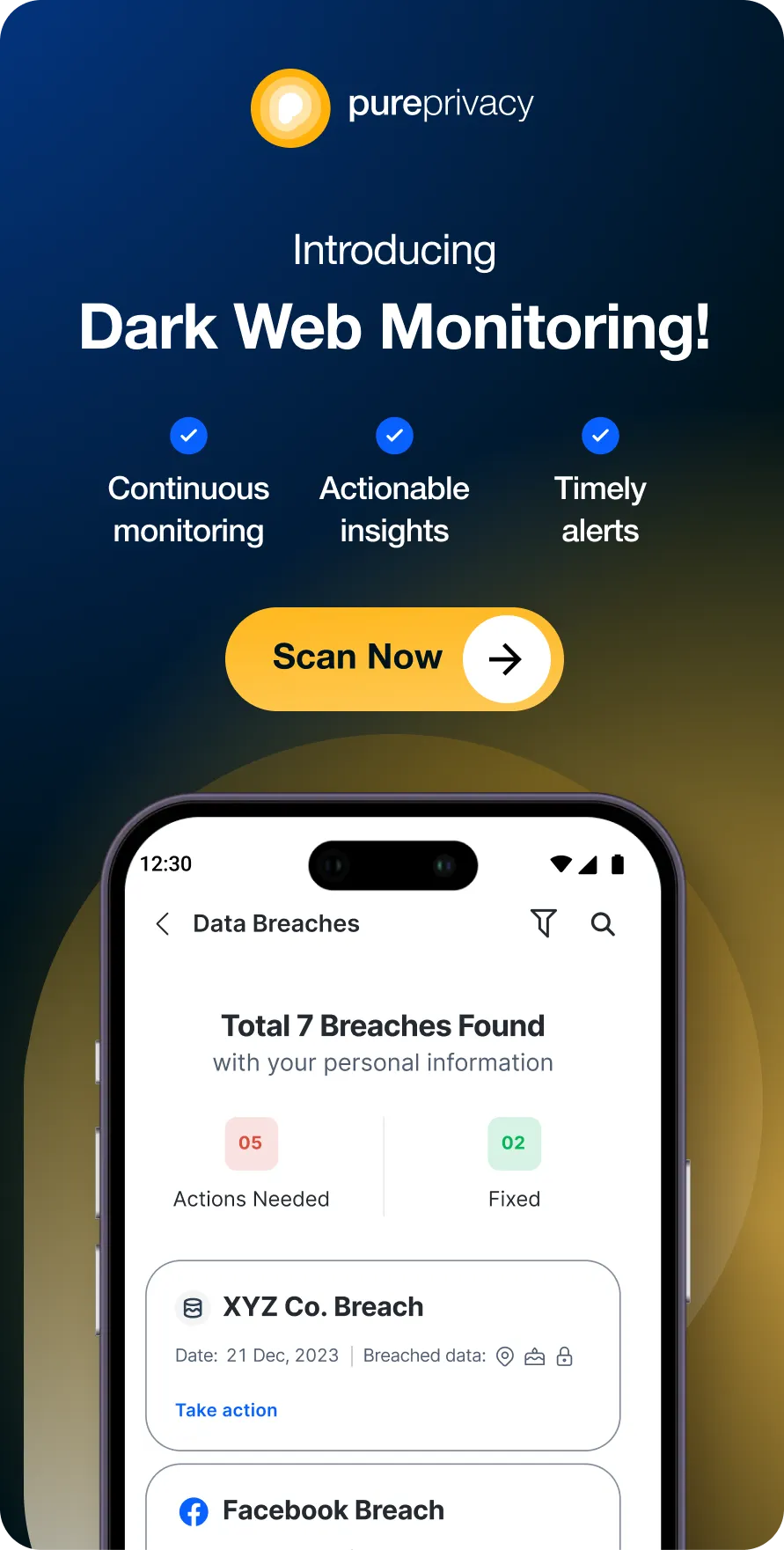
Discover if Your Most Critical Identifiers Have Been Exposed on the Dark Web
Receive timely alerts and actionable insights with PurePrivacy's Dark Web Monitoring.
What Is a Data Breach?
A data breach often refers to an event involving security that results in data getting stolen or made available to unwanted parties.
It might sometimes be accidental, but attackers seeking personal information for crimes such as identity fraud could also purposefully use it.
Data breaches may occur almost anywhere, from big companies to small businesses and even to an individual's details.
How Do Data Breaches Occur?
Data breaches occur when unauthorized individuals access sensitive information, which can happen in a variety of methods. The most common methods by which data breaches happen are as follows:
Human Error
Human errors, including suffering from scams, changing security settings incorrectly, and accidentally sharing sensitive information, are the primary causes of many breaches. Cybercriminals may then take advantage of these to cause accidental data releases.
Weak Passwords
Many breaches use weak or stolen passwords. Cybercriminals rarely use brute force attacks or credential stuffing to compromise accounts with weak or reused passwords.
Software Vulnerabilities
Outdated software and unpatched systems provide opportunities for attackers. Cybercriminals use these vulnerabilities to breach networks and obtain sensitive data.
Malware and Ransomware
These malicious applications can infect systems, encrypt files, or steal data. Ransomware attacks have also become common; they lock organizations out of their data until a ransom is paid.
Insider Threats
This protected information may be sought through negligence or malicious behavior from employees or contractors with access authority. Insider threats are hard to detect since they may already possess permission to access critical data.
Social Engineering
Cybercriminals can use social engineering techniques, such as phishing or fraud, to manipulate people into disclosing sensitive information or providing system access through impersonation. These approaches make use of human psychology rather than technological ones.
Third-Party Risks
If an organization outsources parts of its services to third-party suppliers, a breach may be accidentally enabled by a lack of appropriate security measures. Illegal access to sensitive data is one of the consequences of a third-party service provider security breach.
Lack of Encryption
Unencrypted data, whether it rests or travels across networks, becomes more susceptible to interception and theft.
12 Best Practices for Preventing Data Breaches on Your Own
Employee Education
Training should be provided regularly to enhance knowledge of security threats, such as setting strong passwords and recognizing phishing efforts. Employee education is critical since it may be the first defense against a security intrusion.
Develop and Update Procedures
Establish clear data security policies that are updated regularly. This will assist different staff members in understanding their roles in handling data and access restrictions, fostering a security-conscious culture inside the firm.
Implement Strong Password
Enforce complex passwords and regular password changes. Strong passwords are required to prevent unwanted access to sensitive data.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to identify themselves, which increases the need for additional verification forms before accessing sensitive information. Finally, even if the password is obtained, attackers will need help to get access.
Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encrypt data in transit and at rest to prevent unwanted access. This is especially crucial when sharing sensitive data via networks.
Regular Data Backups
Backup systems may automatically save essential data securely, which can be recovered if a breach occurs. Perform frequent testing to confirm that your data restoration procedure is working correctly.
Limit Access and Monitor the Same
It allows access to sensitive data following the least privilege principle, which states that workers should only get data as needed for their duties. To prevent unwanted access, frequently check and confirm the access permissions.
Physical Data Security
Devices and records are stored in secure locations that are only accessible by authorized individuals, which prevents physical data theft.
Implement Robust Security Software
Firewalls, antivirus, and anti-spyware programs should be installed and updated on systems. Given the continual evolution of threats, these tools require frequent upgrades.
Consult Security Experts
Consider working with providers or employing cybersecurity experts to strengthen your security procedures. Their knowledge might help you locate weak points and successfully implement best practices.
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Assess your safety record regularly to find vulnerabilities and ensure security policy compliance. Taking a proactive approach addresses possible vulnerabilities before they may be exploited.
Incident Response Plan
To ensure the company is prepared for a data breach, regularly create and test an incident response strategy. The plan should specify how to react in the event of a violation.
Protect Yourself from Internet Threats & Breaches
PurePrivacy is a privacy solution that protects your data from scammers and hackers, allowing you to stay safe online:
- Dark Web Monitoring: Monitor the dark web for personally identifying information.
- Tracker Blocker: Prevent data gathering and internet monitoring.
- Remove My Data: Automate data opt-out requests to multiple data brokers.
- Social Privacy Manager: Enhance your privacy on popular social networking sites.
24/7 Monitoring and Alerts for the Dark Web
Stay informed with continuous dark web monitoring and instant alerts for stolen data.
Stop the Trackers to Protect Your Privacy
Prevent websites and third-party trackers from collecting your browsing history.
Send Automated Opt-out Requests
Automatically sends opt-out requests to 200+ data brokers, saving you time and effort.
Enhance Your Social Network Privacy Level
Enhance your online security by optimizing privacy settings on social networks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
How do you manage breaches of data?

Companies that experience data breaches should act quickly to address the incident by alerting the parties impacted and putting preventative measures in place. Working together with legal and cybersecurity specialists is essential to managing the issue well and limiting harm.
-
What is the largest data breach ever recorded?

A major breach of data known as the "Mother of All Breaches" (MOAB) was discovered in January 2024 by security researcher Bob Diachenko of Security Discovery. This is one of the most recent breaches to date and is regarded as the largest data breach in history.
-
How does a data breach get detected?

Emails that are returned with questionable content, attempts to log in from unidentified networks, and cache overflows against database servers are common instances of indications. As soon as you discover a data breach, you should take a few safeguards.
-
How are data breaches accessed by hackers?

Hackers can get identities by purchasing stolen credentials from the dark web, employing social engineering techniques to coerce employees into disclosing their passwords, or utilizing brute force assaults to break passwords.
In Conclusion
To avoid being a target victim of identity fraud and financial scams, you should check your credit card statements often and track your credit report.
Being aware of your entire financial situation can highlight fraudulent online activities before the damage is done.
Reduce your risk of data breaches by taking easy precautions like using strong passwords, updating your software, and protecting your online activities with PurePrivacy with a VPN.